Networking
Switching, Routing and Gateways
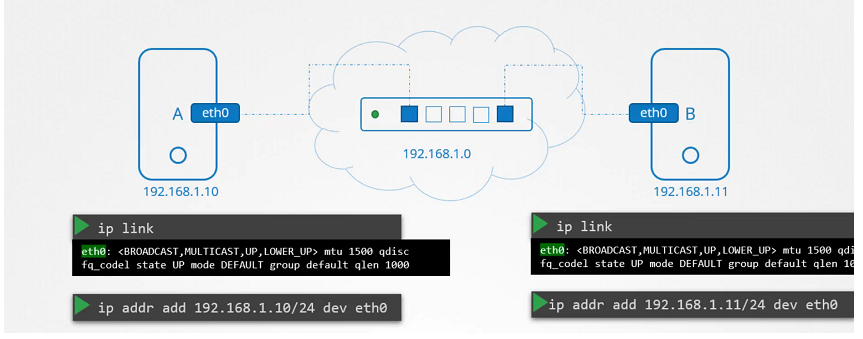
Switching
To see the interface on the host system
$ ip link
To see the IP Address interfaces.
$ ip addr
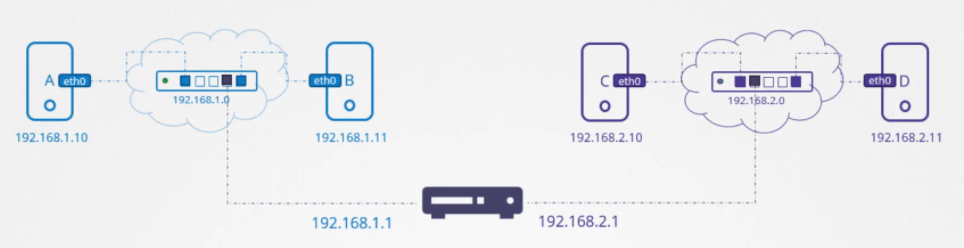
Routing
To see the existing routing table on the host system.
$ route
$ ip route show
or
$ ip route list
- To add entries into the routing table.
$ ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.2.1
Gateways
To add a default route.
$ ip route add default via 192.168.2.1
To check the IP forwarding is enabled on the host.
$ cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
0
$ echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Enable packet forwarding for IPv4.
$ cat /etc/sysctl.conf
# Uncomment the line
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
To view the sysctl variables.
$ sysctl -a
To reload the sysctl configuration.
$ sysctl --system
Name resolution
With help of the ping command. Checking the reachability of the IP Addr on the Network.
$ ping 172.17.0.64
PING 172.17.0.64 (172.17.0.64) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.17.0.64: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.384 ms
64 bytes from 172.17.0.64: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.415 ms
Checking with their hostname
$ ping web
ping: unknown host web
Adding entry in the /etc/hosts file to resolve by their hostname.
$ cat >> /etc/hosts
172.17.0.64 web
# Ctrl + c to exit
It will look into the /etc/hosts file.
$ ping web
PING web (172.17.0.64) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from web (172.17.0.64): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.491 ms
64 bytes from web (172.17.0.64): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.636 ms
$ ssh web
$ curl http://web
DNS
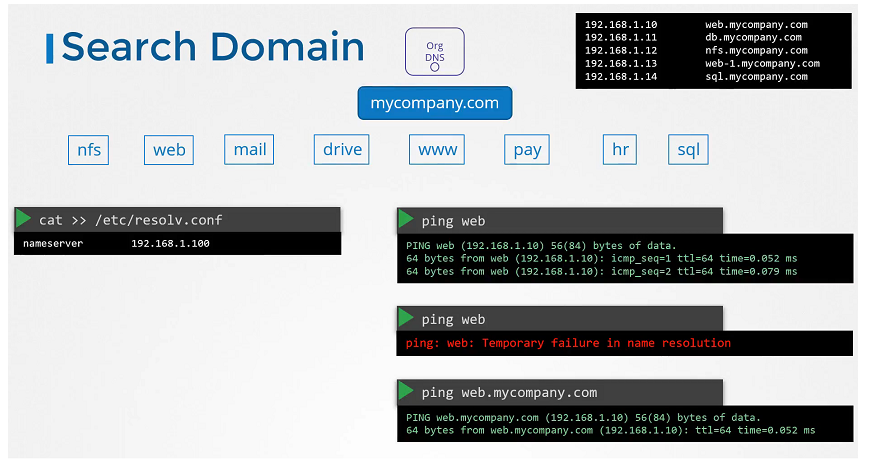
Every host has a DNS resolution configuration file at /etc/resolv.conf.
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 127.0.0.53
options edns0
To change the order of dns resolution, we need to do changes into the /etc/nsswitch.conf file.
$ cat /etc/nsswitch.conf
hosts: files dns
networks: files
If it fails in some conditions.
$ ping wwww.github.com
ping: www.github.com: Temporary failure in name resolution
Adding well known public nameserver in the /etc/resolv.conf file.
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 127.0.0.53
nameserver 8.8.8.8
options edns0
$ ping www.github.com
PING github.com (140.82.121.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 140.82.121.3 (140.82.121.3): icmp_seq=1 ttl=57 time=7.07 ms
64 bytes from 140.82.121.3 (140.82.121.3): icmp_seq=2 ttl=57 time=5.42 ms
Domain name
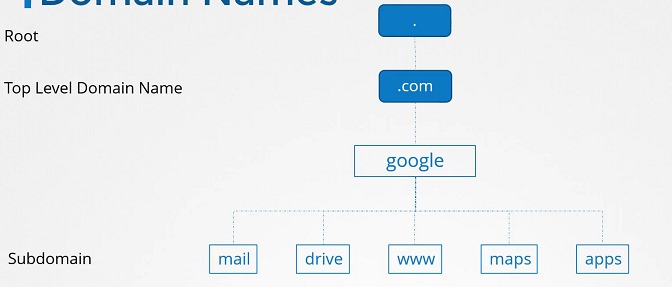
Networking tools
Useful networking tools to test dns name resolution.
nslookup
$ nslookup www.google.com
Server: 127.0.0.53
Address: 127.0.0.53#53
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: www.google.com
Address: 172.217.18.4
Name: www.google.com
dig
$ dig www.google.com
; <<>> DiG 9.11.3-1 ...
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 8738
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 65494
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.google.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.google.com. 63 IN A 216.58.206.4
;; Query time: 6 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.53#53(127.0.0.53)
$ wget https://github.com/coredns/coredns/releases/download/v1.7.0/coredns_1.7.0_linux_amd64.tgz
coredns_1.7.0_linux_amd64.tgz
$ tar -xzvf coredns_1.7.0_linux_amd64.tgz
coredns
Core DNS
$ wget https://github.com/coredns/coredns/releases/download/v1.7.0/coredns_1.7.0_linux_amd64.tgz
coredns_1.7.0_linux_amd64.tgz
$ tar -xzvf coredns_1.7.0_linux_amd64.tgz
Run the executable file to start a DNS server. By default, it’s listen on port 53, which is the default port for a DNS server.
$ ./coredns
Configuring the hosts file
- Adding entries into the
/etc/hostsfile. - CoreDNS will pick the ips and names from the
/etc/hostsfile on the server.
$ cat > /etc/hosts
192.168.1.10 web
192.168.1.11 db
192.168.1.15 web-1
192.168.1.16 db-1
192.168.1.21 web-2
192.168.1.22 db-2
Adding into the Corefile
$ cat > Corefile
. {
hosts /etc/hosts
}
Run the executable file
$ ./coredns
Networking namespaces
Process Namespace
On the container
$ ps aux
On the host
$ ps aux
Network Namespace
$ route
$ arp
Create Network Namespace
$ ip netns add red
$ ip netns add blue
- List the network namespace
$ ip netns
Exec in Network Namespace
- List the interfaces on the host
$ ip link
- Exec inside the network namespace
$ ip netns exec red ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
$ ip netns exec blue ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
- You can try with other options as well. Both works the same.
$ ip -n red link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
ARP and Routing Table
On the host
$ arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
172.17.0.21 ether 02:42:ac:11:00:15 C ens3
172.17.0.55 ether 02:42:ac:11:00:37 C ens3
On the Network Namespace
$ ip netns exec red arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
$ ip netns exec blue arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
On the host
$ route
On the Network Namespace
$ ip netns exec red route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
$ ip netns exec blue route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
Virtual Cable
- To create a virtual cable
$ ip link add veth-red type veth peer name veth-blue
- To attach with the network namespaces
$ ip link set veth-red netns red
$ ip link set veth-blue netns blue
- To add an IP address
$ ip -n red addr add 192.168.15.1/24 dev veth-red
$ ip -n blue addr add 192.168.15.2/24 dev veth-blue
- To turn it up
nsinterfaces
$ ip -n red link set veth-red up
$ ip -n blue link set veth-blue up
- Check the reachability
$ ip netns exec red ping 192.168.15.2
PING 192.168.15.2 (192.168.15.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.15.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.035 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.15.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.046 ms
$ ip netns exec red arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
192.168.15.2 ether da:a7:29:c4:5a:45 C veth-red
$ ip netns exec blue arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
192.168.15.1 ether 92:d1:52:38:c8:bc C veth-blue
- Delete the link.
$ ip -n red link del veth-red
On the host
# Not available
$ arp
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface
172.16.0.72 ether 06:fe:61:1a:75:47 C ens3
172.17.0.68 ether 02:42:ac:11:00:44 C ens3
172.17.0.74 ether 02:42:ac:11:00:4a C ens3
172.17.0.75 ether 02:42:ac:11:00:4b C ens3
Linux Bridge
- Create a network namespace
$ ip netns add red
$ ip netns add blue
- To create a internal virtual bridge network, we add a new interface to the host
$ ip link add v-net-0 type bridge
- Display in the host
$ ip link
8: v-net-0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether fa:fd:d4:9b:33:66 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- Currently it’s down, so turn it up
$ ip link set dev v-net-0 up
- To connect network namespace to the bridge. Creating a virtual cabel
$ ip link add veth-red type veth peer name veth-red-br
$ ip link add veth-blue type veth peer name veth-blue-br
- Set with the network namespaces
$ ip link set veth-red netns red
$ ip link set veth-blue netns blue
$ ip link set veth-red-br master v-net-0
$ ip link set veth-blue-br master v-net-0
- To add an IP address
$ ip -n red addr add 192.168.15.1/24 dev veth-red
$ ip -n blue addr add 192.168.15.2/24 dev veth-blue
- To turn it up
nsinterfaces
$ ip -n red link set veth-red up
$ ip -n blue link set veth-blue up
- To add an IP address
$ ip addr add 192.168.15.5/24 dev v-net-0
- Turn it up added interfaces on the host
$ ip link set dev veth-red-br up
$ ip link set dev veth-blue-br up
On the host
$ ping 192.168.15.1
On the ns
$ ip netns exec blue ping 192.168.1.1
Connect: Network is unreachable
$ ip netns exec blue route
$ ip netns exec blue ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.15.5
# Check the IP Address of the host
$ ip a
$ ip netns exec blue ping 192.168.1.1
PING 192.168.1.1 (192.168.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
$ iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.15.0/24 -j MASQUERADE
$ ip netns exec blue ping 192.168.1.1
$ ip netns exec blue ping 8.8.8.8
$ ip netns exec blue route
$ ip netns exec blue ip route add default via 192.168.15.5
$ ip netns exec blue ping 8.8.8.8
- Adding port forwarding rule to the iptables
$ iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING --dport 80 --to-destination 192.168.15.2:80 -j DNAT
$ iptables -nvL -t nat
Docker networking
None Network
- Running docker container with
nonenetwork
$ docker run --network none nginx
Host Network
- Running docker container with
hostnetwork
$ docker run --network host nginx
Bridge Network
- Running docker container with
bridgenetwork
$ docker run --network bridge nginx
List the Docker Network
$ docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
4974cba36c8e bridge bridge local
0e7b30a6c996 host host local
a4b19b17d2c5 none null local
To view the Network Device on the Host
$ ip link
or
$ ip link show docker0
3: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:cf:c3:df:f5 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- With the help of
ip link addcommand to type setbridgetodocker0
$ ip link add docker0 type bridge
To view the IP Addr of the interface docker0
$ ip addr
or
$ ip addr show docker0
3: docker0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state DOWN group default
link/ether 02:42:cf:c3:df:f5 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.18.0.1/24 brd 172.18.0.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Run the command to create a Docker Container
$ docker run nginx
To list the Network Namespace
$ ip netns
1c452d473e2a (id: 2)
db732004aa9b (id: 1)
04acb487a641 (id: 0)
default
# Inspect the Docker Container
$ docker inspect <container-id>
# To view the interface attached with the local bridge docker0
$ ip link
3: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether 02:42:c8:3a:ea:67 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: vetha3e33331@if3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master docker0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether e2:b2:ad:c9:8b:98 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
# with -n options with the network namespace to view the other end of the interface
$ ip -n 04acb487a641 link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
3: eth0@if5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether c6:f3:ca:12:5e:74 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
# To view the IP Addr assigned to this interface
$ ip -n 04acb487a641 addr
3: eth0@if5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether c6:f3:ca:12:5e:74 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.244.0.2/24 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Port Mapping
- Creating a docker container.
$ docker run -itd --name nginx nginx
d74ca9d57c1d8983db2c590df2fdd109e07e1972d6b361a6ecad8a942af5bf7e
- Inspect the docker container to view the IPAddress.
$ docker inspect nginx | grep -w IPAddress
"IPAddress": "172.18.0.6",
"IPAddress": "172.18.0.6",
- Accessing web page with the
curlcommand.
$ curl --head http://172.18.0.6:80
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.19.2
- Port Mapping to docker container
$ docker run -itd --name nginx -p 8080:80 nginx
e7387bbb2e2b6cc1d2096a080445a6b83f2faeb30be74c41741fe7891402f6b6
- Inspecting docker container to view the assgined ports.
$ docker inspect nginx | grep -w -A5 Ports
"Ports": {
"80/tcp": [
{
"HostIp": "0.0.0.0",
"HostPort": "8080"
}
- To view the IP Addr of the host system
$ ip a
# Accessing nginx page with curl command
$ curl --head http://192.168.10.11:8080
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.19.2
- Configuring iptables nat rules
$ iptables \
-t nat \
-A PREROUTING \
-j DNAT \
--dport 8080 \
--to-destination 80
$ iptables \
-t nat \
-A DOCKER \
-j DNAT \
--dport 8080 \
--to-destination 172.18.0.6:80
List the Iptables rules
$ iptables -nvL -t nat
Cluster Networking
-
The “pod-to-pod network” or “pod network”:
-
provides communication between pods and nodes
-
is generally implemented with CNI plugins
-
-
The “pod-to-service network”:
-
provides internal communication and load balancing
-
is generally implemented with kube-proxy (or maybe kube-router)
-
-
Network policies:
-
provide firewalling and isolation
-
can be bundled with the “pod network” or provided by another component
-
In this section, we will take a look at Pre-requisite of the Cluster Networking
- Set the unique hostname.
- Get the IP addr of the system (master and worker node).
- Check the Ports.
IP and Hostname
- To view the hostname
$ hostname
- To view the IP addr of the system
$ ip a
Set the hostname
$ hostnamectl set-hostname <host-name>
$ exec bash
View the Listening Ports of the system
$ netstat -nltp
Pod Networking
In this section, we will take a look at Pod Networking
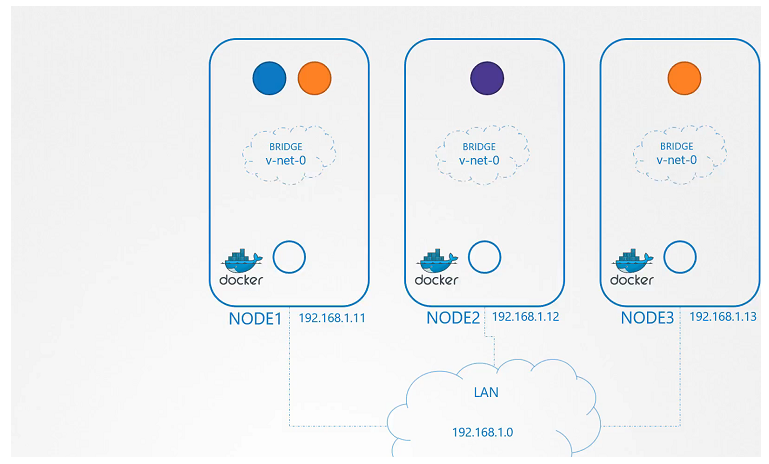
- To add bridge network on each node
node01
$ ip link add v-net-0 type bridge
node02
$ ip link add v-net-0 type bridge
node03
$ ip link add v-net-0 type bridge
- Currently it’s down, turn it up.
node01
$ ip link set dev v-net-0 up
node02
$ ip link set dev v-net-0 up
node03
$ ip link set dev v-net-0 up
- Set the IP Addr for the bridge interface
node01
$ ip addr add 10.244.1.1/24 dev v-net-0
node02
$ ip addr add 10.244.2.1/24 dev v-net-0
node03
$ ip addr add 10.244.3.1/24 dev v-net-0
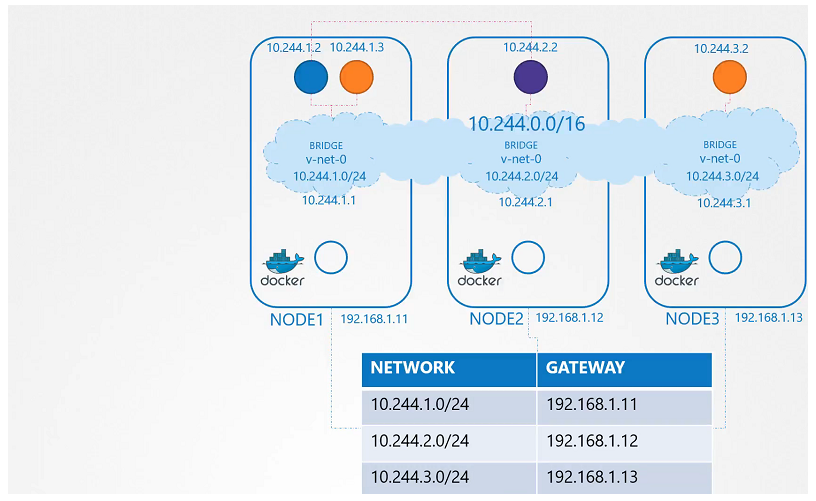
- heck the reachability
$ ping 10.244.2.2
Connect: Network is unreachable
- Add route in the routing table
$ ip route add 10.244.2.2 via 192.168.1.12
node01
$ ip route add 10.244.2.2 via 192.168.1.12
$ ip route add 10.244.3.2 via 192.168.1.13
node02
$ ip route add 10.244.1.2 via 192.168.1.11
$ ip route add 10.244.3.2 via 192.168.1.13
node03
$ ip route add 10.244.1.2 via 192.168.1.11
$ ip route add 10.244.2.2 via 192.168.1.12
- Add a single large network
CNI
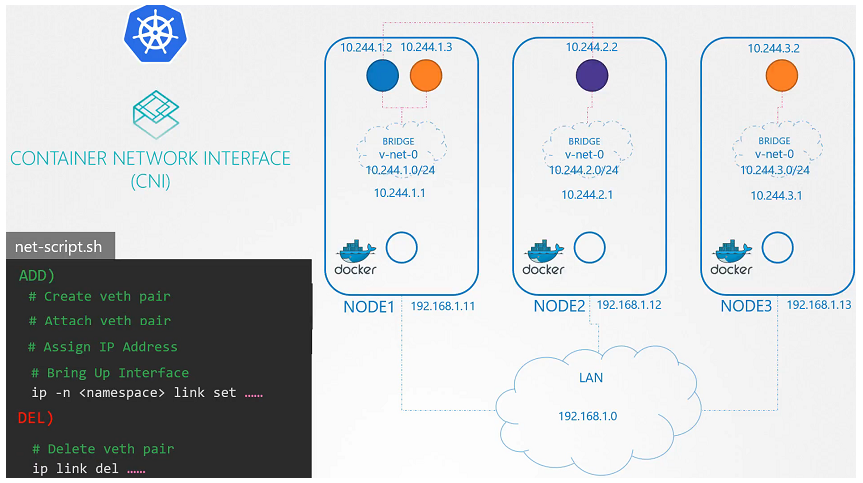
CNI in Kubernetes
In this section, we will take a look at Pre-requisite Container Network Interface(CNI)
$ ls /opt/cni/bin/
bridge dhcp flannel host-device host-local ipvlan loopback macvlan portmap ptp sample tuning vlan
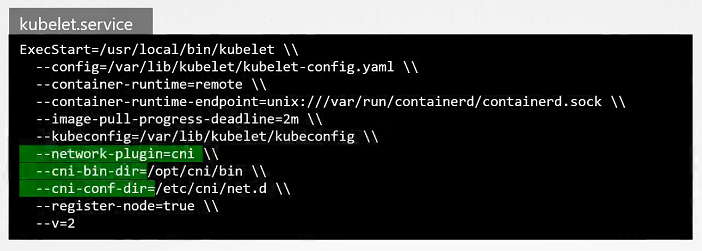
- Check the status of the Kubelet Service
$ systemctl status kubelet.service
View Kubelet Options
$ ps -aux | grep kubelet
Check the Supportable Plugins
- To check the all supportable plugins available in the
/opt/cni/bindirectory.
$ ls /opt/cni/bin
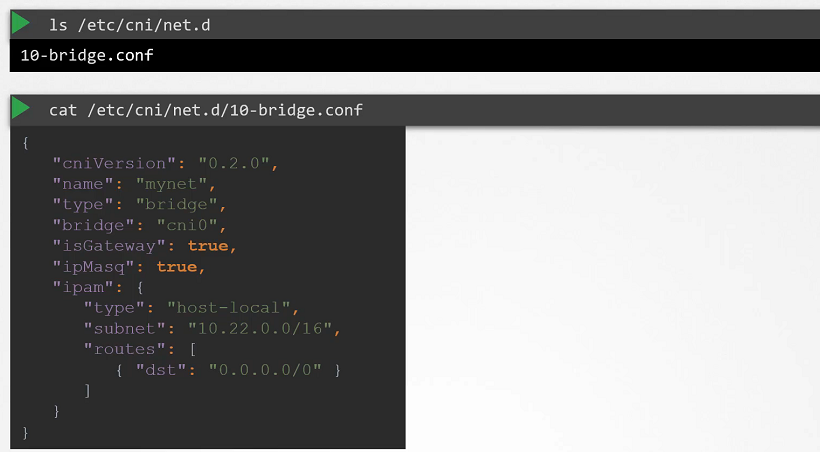
Check the CNI Plugins
- To check the cni plugins which kubelet needs to be used.
ls /etc/cni/net.d
CNI Weave
In this section, we will take a look at “CNI Weave in the Kubernetes Cluster”
Deploy Weave
- Installing weave net onto the Kubernetes cluster with a single command.
$ kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
serviceaccount/weave-net created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
daemonset.apps/weave-net created
Weave Peers
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-66bff467f8-894jf 1/1 Running 0 52m
coredns-66bff467f8-nck5f 1/1 Running 0 52m
etcd-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 52m
kube-apiserver-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 52m
kube-controller-manager-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 52m
kube-keepalived-vip-mbr7d 1/1 Running 0 52m
kube-proxy-p2mld 1/1 Running 0 52m
kube-proxy-vjcwp 1/1 Running 0 52m
kube-scheduler-controlplane 1/1 Running 0 52m
weave-net-jgr8x 2/2 Running 0 45m
weave-net-tb9tz 2/2 Running 0 45m
View the logs of Weave Pod’s
$ kubectl logs weave-net-tb9tz weave -n kube-system
View the default route in the Pod
$ kubectl run test --image=busybox --command -- sleep 4500
pod/test created
$ kubectl exec test -- ip route
default via 10.244.1.1 dev eth0
IPAM Weave (IP Adress management)
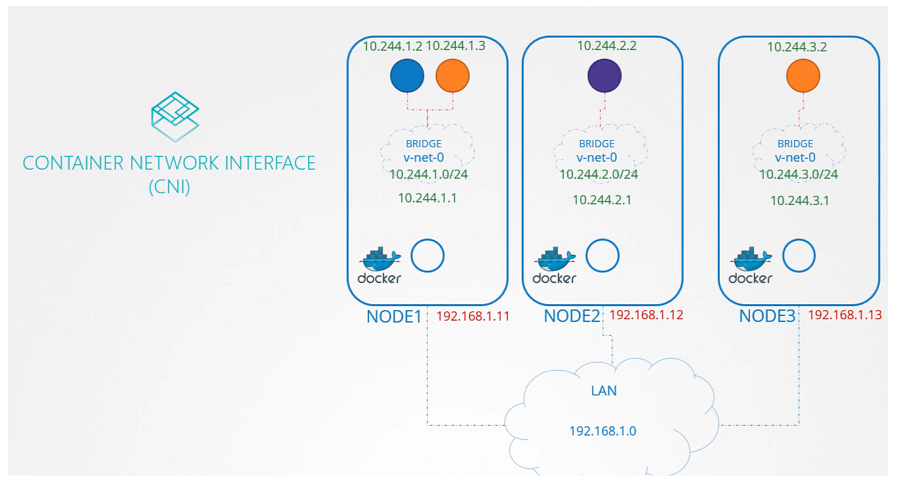
- How weaveworks Manages IP addresses in the Kubernetes Cluster
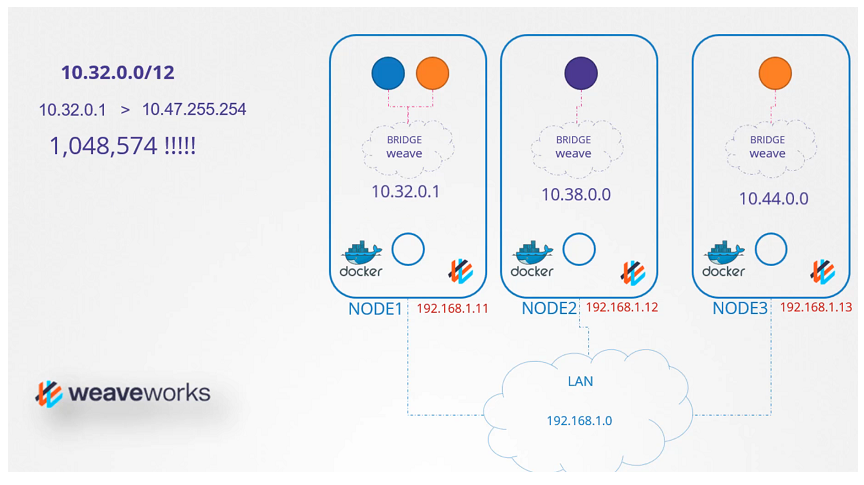
Service networking
Service Types
- ClusterIP
clusterIP.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: local-cluster
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx- NodePort
nodeportIP.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nodeport-wide
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginxTo create the service
$ kubectl create -f clusterIP.yaml
service/local-cluster created
$ kubectl create -f nodeportIP.yaml
service/nodeport-wide created
To get the Additional Information
$ kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx 1/1 Running 0 1m 10.244.1.3 node01 <none> <no
To get the Service
$ kubectl get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
Kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 5m22s
local-cluster ClusterIP 10.101.67.139 <none> 80/TCP 3m
nodeport-wide NodePort 10.102.29.204 <none> 80:30016/TCP 2m
To check the Service Cluster IP Range
$ ps -aux | grep kube-apiserver
--secure-port=6443 --service-account-key-file=/etc/Kubernetes/pki/sa.pub --
service-cluster-ip-range=10.96.0.0/12
To check the rules created by kube-proxy in the iptables
$ iptables -L -t nat | grep local-cluster
KUBE-MARK-MASQ all -- 10.244.1.3 anywhere /* default/local-cluster: */
DNAT tcp -- anywhere anywhere /* default/local-cluster: */ tcp to:10.244.1.3:80
KUBE-MARK-MASQ tcp -- !10.244.0.0/16 10.101.67.139 /* default/local-cluster: cluster IP */ tcp dpt:http
KUBE-SVC-SDGXHD6P3SINP7QJ tcp -- anywhere 10.101.67.139 /* default/local-cluster: cluster IP */ tcp dpt:http
KUBE-SEP-GEKJR4UBUI5ONAYW all -- anywhere anywhere /* default/local-cluster: */
To check the logs of kube-proxy
- May this file location is vary depends on your installation process.
$ cat /var/log/kube-proxy.log
DNS in K8S
Pod DNS Record
- The following DNS resolution:
<POD-IP-ADDRESS>.<namespace-name>.pod.cluster.local
Example
# Pod is located in a default namespace
10-244-1-10.default.pod.cluster.local
# To create a namespace
$ kubectl create ns apps
# To create a Pod
$ kubectl run nginx --image=nginx --namespace apps
# To get the additional information of the Pod in the namespace "apps"
$ kubectl get po -n apps -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx 1/1 Running 0 99s 10.244.1.3 node01 <none> <none>
# To get the dns record of the nginx Pod from the default namespace
$ kubectl run -it test --image=busybox:1.28 --rm --restart=Never -- nslookup 10-244-1-3.apps.pod.cluster.local
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: 10-244-1-3.apps.pod.cluster.local
Address 1: 10.244.1.3
pod "test" deleted
# Accessing with curl command
$ kubectl run -it nginx-test --image=nginx --rm --restart=Never -- curl -Is http://10-244-1-3.apps.pod.cluster.local
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.19.2
Service DNS Record
- The following DNS resolution:
<service-name>.<namespace-name>.svc.cluster.local
Example
# Service is located in a default namespace
web-service.default.svc.cluster.local
- Pod, Service is located in the
appsnamespace
# Expose the nginx Pod
$ kubectl expose pod nginx --name=nginx-service --port 80 --namespace apps
service/nginx-service exposed
# Get the nginx-service in the namespace "apps"
$ kubectl get svc -n apps
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-service ClusterIP 10.96.120.174 <none> 80/TCP 6s
# To get the dns record of the nginx-service from the default namespace
$ kubectl run -it test --image=busybox:1.28 --rm --restart=Never -- nslookup nginx-service.apps.svc.cluster.local
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: nginx-service.apps.svc.cluster.local
Address 1: 10.96.120.174 nginx-service.apps.svc.cluster.local
pod "test" deleted
# Accessing with curl command
$ kubectl run -it nginx-test --image=nginx --rm --restart=Never -- curl -Is http://nginx-service.apps.svc.cluster.local
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.19.2
CoreDNS in K8s
To view the Pod
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-66bff467f8-2vghh 1/1 Running 0 53m
coredns-66bff467f8-t5nzm 1/1 Running 0 53m
To view the Deployment
$ kubectl get deployment -n kube-system
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
coredns 2/2 2 2 53m
To view the configmap of CoreDNS
$ kubectl get configmap -n kube-system
NAME DATA AGE
coredns 1 52m
CoreDNS Configuration File
$ kubectl describe cm coredns -n kube-system
Corefile:
---
.:53 {
errors
health { lameduck 5s
}
ready
Kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa {
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
ttl 30
}
prometheus :9153
forward . /etc/resolv.conf
cache 30
loop
reload
}To view the Service
$ kubectl get service -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 62m
To view Configuration into the kubelet
$ cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml | grep -A2 clusterDNS
clusterDNS:
- 10.96.0.10
clusterDomain: cluster.local
To view the fully qualified domain name
- With the
hostcommand, we will get fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
$ host web-service
web-service.default.svc.cluster.local has address 10.106.112.101
$ host web-service.default
web-service.default.svc.cluster.local has address 10.106.112.101
$ host web-service.default.svc
web-service.default.svc.cluster.local has address 10.106.112.101
$ host web-service.default.svc.cluster.local
web-service.default.svc.cluster.local has address 10.106.112.101
To view the /etc/resolv.conf file
$ kubectl run -it --rm --restart=Never test-pod --image=busybox -- cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 10.96.0.10
search default.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local
options ndots:5
pod "test-pod" deleted
Resolve the Pod
$ kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
test-pod 1/1 Running 0 11m 10.244.1.3 node01 <none> <none>
nginx 1/1 Running 0 10m 10.244.1.4 node01 <none> <none>
$ kubectl exec -it test-pod -- nslookup 10-244-1-4.default.pod.cluster.local
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: 10-244-1-4.default.pod.cluster.local
Address 1: 10.244.1.4
Resolve the Service
$ kubectl get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
Kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 85m
web-service ClusterIP 10.106.112.101 <none> 80/TCP 9m
$ kubectl exec -it test-pod -- nslookup web-service.default.svc.cluster.local
Server: 10.96.0.10
Address 1: 10.96.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: web-service.default.svc.cluster.local
Address 1: 10.106.112.101 web-service.default.svc.cluster.local
ConfigMap
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-configuration
Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ingress-controller
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: nginx-ingress
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
serviceAccountName: ingress-serviceaccount
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: quay.io/Kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.21.0
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443ServiceAccount
- ServiceAccount require for authentication purposes along with correct Roles, ClusterRoles and RoleBindings.
- Create a ingress service account
$ kubectl create -f ingress-sa.yaml
serviceaccount/ingress-serviceaccount created
Service Type - NodePort
# service-Nodeport.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
name: http
- port: 443
targetPort: 443
protocol: TCP
name: https
selector:
name: nginx-ingress- Create a service
$ kubectl create -f service-Nodeport.yaml
- To get the service
$ kubectl get service
Ingress Resources
Ingress-wear.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-wear
spec:
backend:
serviceName: wear-service
servicePort: 80- To create the ingress resource
$ kubectl create -f Ingress-wear.yaml
ingress.extensions/ingress-wear created
- To get the ingress
$ kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-wear <none> * 80 18s
Ingress Resource - Rules
- 1 Rule and 2 Paths.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-wear-watch
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /wear
backend:
serviceName: wear-service
servicePort: 80
- path: /watch
backend:
serviceName: watch-service
servicePort: 80- Describe the earlier created ingress resource
$ kubectl describe ingress ingress-wear-watch
Name: ingress-wear-watch
Namespace: default
Address:
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<none>)
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
*
/wear wear-service:80 (<none>)
/watch watch-service:80 (<none>)
Annotations: <none>
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal CREATE 23s nginx-ingress-controller Ingress default/ingress-wear-watch
- 2 Rules and 1 Path each.
# Ingress-wear-watch.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-wear-watch
spec:
rules:
- host: wear.my-online-store.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: wear-service
servicePort: 80
- host: watch.my-online-store.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: watch-service
servicePort: 80ingress annotation
In this section, we will take a look at Ingress annotations and rewrite-target
- Different Ingress controllers have different options to customize the way it works. Nginx Ingress Controller has many options but we will take a look into the one of the option “Rewrite Target” option.
- Kubernetes Version 1.18
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
namespace: critical-space
annotations:
nginx.ingress.Kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /pay
backend:
serviceName: pay-service
servicePort: 8282Demo: Installing the Calico Network Plugin
$ minikube stop; minikube delete
$ minikube start --network-plugin=cni --extra-config=kubeadm.pod-network-cidr=10.10.0.0/16
$ kubectl create -f [<https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/tigera-operator.yaml>](<https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/tigera-operator.yaml>)
$ kubectl api-resources I grep tigera
$ kubectl get pods -n tigera-operator tigera-operator-xxx-yyy
$ wget [<https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/custom-resources.yaml>](<https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/custom-resources.yaml>)
$ sed -i -e s/192.168.0.0/10.10.0.0/g custom-resources.yaml
$ kubectl get installation -o yaml
$ kubectl get pods -n calico-system